力扣算法面试必考精华版75题
数组 / 字符串
交替合并字符串
给你两个字符串 word1 和 word2 。请你从 word1 开始,通过交替添加字母来合并字符串。如果一个字符串比另一个字符串长,就将多出来的字母追加到合并后字符串的末尾。
返回 合并后的字符串 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 public class test { public static void main (String[] args) { System.out.println(mergeAlternately("abc" ,"pqr" )); System.out.println(mergeAlternately("ab" ,"pqrs" )); System.out.println(mergeAlternately("abcd" ,"pq" )); } public static String mergeAlternately (String word1, String word2) { StringBuilder strBuild = new StringBuilder (); int index1 = 0 , index2 = 0 ; while (index1 < word1.length() || index2 < word2.length()){ if (index1 < word1.length()){ strBuild.append(word1.charAt(index1++)); } if (index2 < word2.length()){ strBuild.append(word2.charAt(index2++)); } } return strBuild.toString(); } }
字符串的最大公因子
对于字符串 s 和 t,只有在 s = t + … + t(t 自身连接 1 次或多次)时,我们才认定 “t 能除尽 s”。
给定两个字符串 str1 和 str2 。返回 最长字符串 x,要求满足 x 能除尽 str1 且 x 能除尽 str2 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 public class test { public static void main (String[] args) { System.out.println(gcdOfStrings("ABCABC" ,"ABC" )); System.out.println(gcdOfStrings("ABABAB" ,"ABAB" )); System.out.println(gcdOfStrings("LEET" ,"CODE" )); } public static String gcdOfStrings (String str1, String str2) { StringBuilder strBuild = new StringBuilder (); String result = "" ; for (int i = 0 ; i < Math.min(str1.length(),str2.length()); i++) { if (str1.charAt(i) == str2.charAt(i)){ strBuild.append(str1.charAt(i)); if (check(strBuild.toString(),str1,str2)) result = strBuild.toString(); } } return result; } public static boolean check (String checkStr,String str1, String str2) { if (str1.length()%checkStr.length()!=0 || str2.length()%checkStr.length()!=0 ) return false ; StringBuilder strBuild = new StringBuilder (); for (int i = 0 ; i < str1.length()/checkStr.length(); i++) { strBuild.append(checkStr); } if (!strBuild.toString().equals(str1)) return false ; strBuild = new StringBuilder (); for (int i = 0 ; i < str2.length()/checkStr.length(); i++) { strBuild.append(checkStr); } if (!strBuild.toString().equals(str2)) return false ; return true ; } }
拥有最多糖果的孩子
给你一个数组 candies 和一个整数 extraCandies ,其中 candies[i] 代表第 i 个孩子拥有的糖果数目。
对每一个孩子,检查是否存在一种方案,将额外的 extraCandies 个糖果分配给孩子们之后,此孩子有 最多 的糖果。注意,允许有多个孩子同时拥有 最多 的糖果数目。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 public class test { public static void main (String[] args) { System.out.println(kidsWithCandies(new int []{2 , 3 , 5 , 1 , 3 },3 )); System.out.println(kidsWithCandies(new int []{4 , 2 , 1 , 1 , 2 },1 )); System.out.println(kidsWithCandies(new int []{12 , 1 , 12 },10 )); } public static List<Boolean> kidsWithCandies (int [] candies, int extraCandies) { int max = candies[0 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i < candies.length; i++) { if (max < candies[i]){ max = candies[i]; } } List<Boolean> res = new ArrayList <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < candies.length; i++) { res.add(candies[i]+extraCandies>=max); } return res; } }
种花问题
假设有一个很长的花坛,一部分地块种植了花,另一部分却没有。可是,花不能种植在相邻的地块上,它们会争夺水源,两者都会死去。
给你一个整数数组 flowerbed 表示花坛,由若干 0 和 1 组成,其中 0 表示没种植花,1 表示种植了花。另有一个数 n ,能否在不打破种植规则的情况下种入 n 朵花?能则返回 true ,不能则返回 false 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 public class test { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(canPlaceFlowers(new int[]{1,0,0,0,1},1)); // true System.out.println(canPlaceFlowers(new int[]{1,0,0,0,1},2)); // false } public static boolean canPlaceFlowers(int[] flowerbed, int n) { int num = flowerbed.length; if (n==0) return true; if (num==1) return flowerbed[0] == 0; for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) { if (i==0){ if (flowerbed[1]==0 && flowerbed[0] == 0){ flowerbed[0] = 1; n--; } }else if (i==num-1){ if (flowerbed[num-2]==0 && flowerbed[num-1]==0){ flowerbed[num-1] = 1; n--; } }else{ if (flowerbed[i-1]==0 && flowerbed[i+1]==0 && flowerbed[i]==0){ flowerbed[i] = 1; n--; } } } return !(n>0); } }
双指针
移动零
给定一个数组 nums,编写一个函数将所有 0 移动到数组的末尾,同时保持非零元素的相对顺序。
请注意 ,必须在不复制数组的情况下原地对数组进行操作。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 public class test { public static void main (String[] args) { int [] test1 = new int []{0 ,1 ,0 ,3 ,12 }; moveZeroes(test1); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(test1)); int [] test2 = new int []{0 }; moveZeroes(test2); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(test2)); } public static void moveZeroes (int [] nums) { int zeroJ = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++) { if (nums[i]!=0 ){ nums[zeroJ++] = nums[i]; } } for (int i = zeroJ; i < nums.length; i++) { nums[i] = 0 ; } } }
codetop网站题目
146.LRU缓存(中等)
请你设计并实现一个满足 LRU (最近最少使用) 缓存 约束的数据结构。
LRUCache(int capacity) 以 正整数 作为容量 capacity 初始化 LRU 缓存
int get(int key) 如果关键字 key 存在于缓存中,则返回关键字的值,否则返回 -1 。
void put(int key, int value) 如果关键字 key 已经存在,则变更其数据值 value ;如果不存在,则向缓存中插入该组 key-value 。如果插入操作导致关键字数量超过 capacity ,则应该 逐出 最久未使用的关键字。
示例 :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 输入 ["LRUCache", "put", "put", "get", "put", "get", "put", "get", "get", "get"] [[2], [1, 1], [2, 2], [1], [3, 3], [2], [4, 4], [1], [3], [4]] 输出 [null, null, null, 1, null, -1, null, -1, 3, 4] 解释 LRUCache lRUCache = new LRUCache(2); lRUCache.put(1, 1); // 缓存是 {1=1} lRUCache.put(2, 2); // 缓存是 {1=1, 2=2} lRUCache.get(1); // 返回 1 lRUCache.put(3, 3); // 该操作会使得关键字 2 作废,缓存是 {1=1, 3=3} lRUCache.get(2); // 返回 -1 (未找到) lRUCache.put(4, 4); // 该操作会使得关键字 1 作废,缓存是 {4=4, 3=3} lRUCache.get(1); // 返回 -1 (未找到) lRUCache.get(3); // 返回 3 lRUCache.get(4); // 返回 4
实现 :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 public class test { public static void main (String[] args) { LRUCache test = new LRUCache (4 ); test.put(2 ,1 ); test.put(2 ,2 ); test.put(2 ,3 ); System.out.println(test.get(2 )); test.put(1 ,1 ); test.put(4 ,1 ); System.out.println(test.get(2 )); test.put(6 ,3 ); test.put(4 ,1 ); test.put(7 ,9 ); test.put(8 ,6 ); test.put(5 ,10 ); System.out.println(test.get(5 )); System.out.println(test.get(8 )); } } class LRUCache { HashMap<Integer, linkNode> map = new HashMap (); linkNode head; linkNode end; int capacity; int usedLength; public LRUCache (int capacity) { this .capacity = capacity; this .head = new linkNode (); this .end = new linkNode (); head.nextNode = end; end.prevNode = head; } public void put (int key,int value) { linkNode step = new linkNode (); step.key = key; step.value = value; linkNode cacheNode = map.get(key); if (cacheNode==null ){ if (usedLength+1 > capacity){ map.remove(end.getPrevNode().key); removeNode(end.getPrevNode()); }else { usedLength++; } addToHead(step); map.put(key,step); }else { cacheNode.value = value; nodeToTop(cacheNode); map.put(key,cacheNode); } } public int get (int key) { linkNode node = map.get(key); if (node!=null ){ nodeToTop(node); return node.value; } return -1 ; } public void nodeToTop (linkNode linkedStep) { removeNode(linkedStep); addToHead(linkedStep); } public void addToHead (linkNode node) { linkNode temp = head.getNextNode(); temp.setPrevNode(node); node.setNextNode(temp); head.setNextNode(node); node.setPrevNode(head); } public void removeNode (linkNode node) { node.getPrevNode().setNextNode(node.getNextNode()); node.getNextNode().setPrevNode(node.getPrevNode()); node.setPrevNode(null ); node.setNextNode(null ); } class linkNode { linkNode prevNode; linkNode nextNode; int key; int value; public linkNode () { } public void setPrevNode (linkNode prevNode) { this .prevNode = prevNode; } public void setNextNode (linkNode nextNode) { this .nextNode = nextNode; } public linkNode getPrevNode () { return prevNode; } public linkNode getNextNode () { return nextNode; } } }
206.翻转链表(简单)
给你单链表的头节点 head ,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5] 输出:[5,4,3,2,1]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 public class test { public static void main (String[] args) { ListNode test = new ListNode (1 ,new ListNode (2 ,new ListNode (3 ,new ListNode (4 ,new ListNode (5 ,null ))))); test.print(); test = reverseList(test); test.print(); } public static ListNode reverseList (ListNode head) { ListNode index1 = null ; ListNode index2 = head; while (index2 !=null ){ ListNode step = index1; index1 = index2; index2 = index2.next; index1.next = step; } return index1; } public static ListNode reverseList (ListNode head) { if (head.next==null ){ return head; }else { ListNode res = reverseList(head.next); head.next.next = head; head.next = null ; return res; } } } class ListNode { int val; ListNode next; ListNode() {} ListNode(int val) { this .val = val; } ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this .val = val; this .next = next; } void print () { String res = "[" ; ListNode step = this ; while (step!=null ){ res+=step.val+"," ; step = step.next; } res+="]" ; System.out.println(res); } }
3.无重复字符的最长子串(中等)
给定一个字符串 s ,请你找出其中不含有重复字符的 最长子串 的长度。
示例 1:
1 2 3 输入: s = "abcabcbb" 输出: 3 解释: 因为无重复字符的最长子串是 "abc",所以其长度为 3。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 public class test { public static void main (String[] args) { System.out.println(lengthOfLongestSubstring("abcabcbb" )); System.out.println(lengthOfLongestSubstring("bbbbb" )); System.out.println(lengthOfLongestSubstring("pwwkew" )); System.out.println(lengthOfLongestSubstring("abba" )); } public static int lengthOfLongestSubstring (String s) { HashMap<Character,Integer> map = new HashMap (); int max = 0 ; for (int front = 0 ,end = 0 ; front < s.length(); ) { if (map.get(s.charAt(front))!=null ){ end = Math.max(map.get(s.charAt(front))+1 ,end); } map.put(s.charAt(front),front); front++; max = Math.max(max,(front-end)); } return max; } }
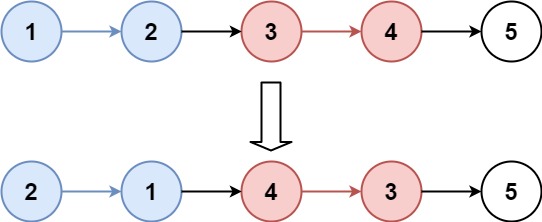
25.K 个一组翻转链表(困难)
给你链表的头节点 head ,每 k 个节点一组进行翻转,请你返回修改后的链表。
k 是一个正整数,它的值小于或等于链表的长度。如果节点总数不是 k 的整数倍,那么请将最后剩余的节点保持原有顺序。
你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际进行节点交换。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2 输出:[2,1,4,3,5]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 public class test { public static void main (String[] args) { ListNode test = new ListNode (1 ,new ListNode (2 ,new ListNode (3 ,new ListNode (4 ,new ListNode (5 ,null ))))); test = reverseKGroup(test,2 ); test.print(); } public static ListNode reverseKGroup (ListNode head, int k) { ListNode prevHead = new ListNode (0 ,head); ListNode stepPrev = prevHead; ListNode stepNext; ListNode step = head; while (true ){ stepNext = getNextINode(step,k); if (stepNext==null ) break ; reverseSmallGroup(stepPrev,stepNext.next,step,k); stepPrev = step; step = step.next; } return prevHead.next; } public static void reverseSmallGroup (ListNode pre,ListNode next,ListNode head,int k) { ListNode index1 = head; ListNode index2 = next; for (int i = 0 ; i < k; i++) { ListNode step = index2; index2 = index1; index1 = index1.next; index2.next = step; } pre.next = index2; } public static ListNode getNextINode (ListNode head, int k) { ListNode step = head; for (int i = 0 ; i < k-1 ; i++) { if (step==null ){ return null ; } step = step.next; } return step; } } class ListNode { int val; ListNode next; ListNode() {} ListNode(int val) { this .val = val; } ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this .val = val; this .next = next; } void print () { String res = "[" ; ListNode step = this ; while (step!=null ){ res+=step.val+"," ; step = step.next; } res+="]" ; System.out.println(res); } }
215.数组中的第K个最大元素(中等)
给定整数数组 nums 和整数 k,请返回数组中第 k 个最大的元素。
请注意,你需要找的是数组排序后的第 k 个最大的元素,而不是第 k 个不同的元素。
你必须设计并实现时间复杂度为 O(n) 的算法解决此问题。
示例 1:
1 2 输入: [3,2,1,5,6,4], k = 2 输出: 5
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 public class test1 { public static void main (String[] args) { int [] a = {1 }; int res = findKthLargest(a,1 ); System.out.println(res); } public static int findKthLargest (int [] nums, int k) { return quickSort(nums,0 ,nums.length-1 ,k); } public static int quickSort (int [] arr, int low, int high, int k) { int i = part(arr,low,high); if (i == arr.length-k){ return arr[i]; }else if (i > arr.length-k){ return quickSort(arr,low,i-1 ,k); }else { return quickSort(arr,i+1 ,high,k); } } public static int part (int [] arr, int low, int high) { int pivot = arr[low]; while (low<high){ while (low<high){ if (pivot >= arr[high]){ arr[low] = arr[high]; low++; break ; }else { high--; } } while (low<high){ if (pivot <= arr[low]){ arr[high] = arr[low]; high--; break ; }else { low++; } } } arr[low] = pivot; return low; } }
15.三数之和(中等)
给你一个整数数组 nums ,判断是否存在三元组 [nums[i], nums[j], nums[k]] 满足 i != j、i != k 且 j != k ,同时还满足 nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[k] == 0 。请
你返回所有和为 0 且不重复的三元组。
注意:答案中不可以包含重复的三元组。
示例 1:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 输入:nums = [-1,0,1,2,-1,-4] 输出:[[-1,-1,2],[-1,0,1]] 解释: nums[0] + nums[1] + nums[2] = (-1) + 0 + 1 = 0 。 nums[1] + nums[2] + nums[4] = 0 + 1 + (-1) = 0 。 nums[0] + nums[3] + nums[4] = (-1) + 2 + (-1) = 0 。 不同的三元组是 [-1,0,1] 和 [-1,-1,2] 。 注意,输出的顺序和三元组的顺序并不重要。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 public class test1 { public static void main (String[] args) { int [] nums = {-1 ,0 ,1 ,2 ,-1 ,-4 }; int [] nums1 = {-1 ,0 ,1 ,0 }; int [] nums2 = {0 ,0 ,0 ,0 }; int [] nums3 = {3 ,-2 ,1 ,0 }; int [] nums4 = {-4 ,-2 ,-1 }; System.out.println(threeSum(nums1)); System.out.println(threeSum(nums2)); System.out.println(threeSum(nums3)); System.out.println(threeSum(nums4)); System.out.println(threeSum(nums)); } public static List<List<Integer>> threeSum (int [] nums) { List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList <>(); if (nums.length<3 || nums == null ) return res; Arrays.sort(nums); if (nums[0 ]>0 ) return res; for (int k = 0 ; k < nums.length-1 && nums[k] <= 0 ;) { for (int i = k + 1 , j = nums.length - 1 ; i != j ;) { if (nums[k] + nums[i] + nums[j] == 0 ){ res.add(List.of(nums[k],nums[i],nums[j])); int n = nums[i]; while (i != j && n == nums[i]){ i++; } }else if (nums[k] + nums[i] + nums[j] < 0 ){ int n = nums[i]; while (i != j && n == nums[i]){ i++; } }else { int n = nums[j]; while (i != j && n == nums[j]){ j--; } } } int n = nums[k]; while (k < nums.length-1 && nums[k] <= 0 && n == nums[k]){ k++; } } return res; } }
53.最大子序和(中等)
给你一个整数数组 nums ,请你找出一个具有最大和的连续子数组(子数组最少包含一个元素),返回其最大和。
子数组 是数组中的一个连续部分。
示例 1:
1 2 3 输入:nums = [-2,1,-3,4,-1,2,1,-5,4] 输出:6 解释:连续子数组 [4,-1,2,1] 的和最大,为 6 。
示例 2:
示例 3:
1 2 输入:nums = [5,4,-1,7,8] 输出:23
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 public class test1 { public static void main (String[] args) { int [] a = {-2 ,1 ,-3 ,4 ,-1 ,2 ,1 ,-5 ,4 }; int res = maxSubArray(a); System.out.println(res); } public static int maxSubArray (int [] nums) { int [] maxSum = {nums[0 ]}; part(nums, nums.length-1 , maxSum); return maxSum[0 ]; } public static int part (int [] nums,int i,int [] max) { if (i==0 ){ return nums[0 ]; }else { int i1 = part(nums,i-1 ,max); max[0 ] = Math.max(max[0 ],i1+nums[i]); max[0 ] = Math.max(max[0 ],nums[i]); return Math.max(i1+nums[i],nums[i]); } } }
912.排序数组(中等)-- 快速排序
给你一个整数数组 nums,请你将该数组升序排列。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:nums = [5,2,3,1] 输出:[1,2,3,5]
示例 2:
1 2 输入:nums = [5,1,1,2,0,0] 输出:[0,0,1,1,2,5]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 public class test1 { public static void main (String[] args) { int [] a = {8 ,2 ,1 ,478 ,32 ,19 ,9 ,612 ,0 ,4 ,-5 ,16 ,75 ,43 ,98 ,21 }; System.out.println(Arrays.toString(sortArray(a))); } public static int [] sortArray(int [] nums) { quickSort(nums,0 ,nums.length-1 ); return nums; } public static void quickSort (int [] nums,int low,int high) { if (low < high){ int n = part(nums,low,high); quickSort(nums,low,n-1 ); quickSort(nums,n+1 ,high); } } public static int part (int [] nums,int low,int high) { int pivot = nums[low]; while (low<high){ while (low < high){ if (nums[high] > pivot){ high--; }else { nums[low] = nums[high]; low++; break ; } } while (low < high){ if (nums[low] < pivot){ low++; }else { nums[high] = nums[low]; high--; break ; } } } nums[low] = pivot; return low; } }
21.合并两个有序链表(简单)
将两个升序链表合并为一个新的 升序 链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:l1 = [1,2,4], l2 = [1,3,4] 输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4]
示例 2:
1 2 输入:l1 = [], l2 = [] 输出:[]
示例 3:
1 2 输入:l1 = [], l2 = [0] 输出:[0]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 public class test1 { public static void main (String[] args) { ListNode l1 = new ListNode (1 ,new ListNode (2 ,new ListNode (4 ))); ListNode l2 = new ListNode (1 ,new ListNode (3 ,new ListNode (4 ))); ListNode lres = mergeTwoLists(l1,l2); printMY(lres); } public static ListNode mergeTwoLists (ListNode list1, ListNode list2) { ListNode res = new ListNode (); ListNode s1 = list1; ListNode s2 = list2; ListNode stepNode = res; while (s1 != null || s2 != null ){ stepNode.next = new ListNode (); stepNode = stepNode.next; if (s2 == null ){ stepNode.val = s1.val; s1 = s1.next; }else if (s1 == null ){ stepNode.val = s2.val; s2 = s2.next; }else if (s1.val <= s2.val){ stepNode.val = s1.val; s1 = s1.next; }else { stepNode.val = s2.val; s2 = s2.next; } } return res.next; } public static void printMY (ListNode list1) { ListNode l1 = list1; StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder (); res.append("ListNode -> [" ); while (l1 != null ){ res.append(l1.val+"," ); l1 = l1.next; } res.append("]" ); System.out.println(res); } } class ListNode { int val; ListNode next; ListNode() {} ListNode(int val) { this .val = val; } ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this .val = val; this .next = next; } }
1.两数之和(简单)
给定一个整数数组 nums 和一个整数目标值 target,请你在该数组中找出 和为目标值 target两个 整数,并返回它们的数组下标。
你可以假设每种输入只会对应一个答案。但是,数组中同一个元素在答案里不能重复出现。
你可以按任意顺序返回答案。
示例 1:
1 2 3 输入:nums = [2,7,11,15], target = 9 输出:[0,1] 解释:因为 nums[0] + nums[1] == 9 ,返回 [0, 1] 。
示例 2:
1 2 输入:nums = [3,2,4], target = 6 输出:[1,2]
示例 3:
1 2 输入:nums = [3,3], target = 6 输出:[0,1]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 public class test1 { public static void main (String[] args) { int [] nums = {2 ,7 ,11 ,15 }; System.out.println(Arrays.toString(twoSum(nums,9 ))); } public static int [] twoSum(int [] nums, int target) { for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++) { for (int j = i+1 ; j < nums.length; j++) { if (nums[i]+nums[j] == target){ return new int []{j,i}; } } } return new int []{}; } public static int [] twoSum(int [] nums, int target) { Map<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++) { map.put(nums[i],i); if (map.containsKey(target - nums[i])){ return new int []{map.get(target - nums[i]),i}; } } return new int []{}; } }
102.二叉树的层序遍历(中等)
给你二叉树的根节点 root ,返回其节点值的 层序遍历 。 (即逐层地,从左到右访问所有节点)。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] 输出:[[3],[9,20],[15,7]]
示例 2:
示例 3:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 public class test1 { public static void main (String[] args) { TreeNode test = new TreeNode (3 ,new TreeNode (9 ),new TreeNode (20 ,new TreeNode (15 ),new TreeNode (7 ))); System.out.println(levelOrder(test)); } public static List<List<Integer>> levelOrder (TreeNode root) { Queue<TreeNode> queue = new ArrayDeque (); List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList <>(); if (root!=null ){ queue.add(root); } while (queue.size()>0 ){ List<Integer> stepArr = new ArrayList <>(); int num = queue.size(); for (int i = 0 ; i < num; i++) { TreeNode step = queue.poll(); if (step.left != null ){ queue.add(step.left); } if (step.right != null ){ queue.add(step.right); } stepArr.add(step.val); } res.add(stepArr); } return res; } } class TreeNode { int val; TreeNode left; TreeNode right; TreeNode() {} TreeNode(int val) { this .val = val; } TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { this .val = val; this .left = left; this .right = right; } }
5.最长回文子串(中等)
给你一个字符串 s,找到 s 中最长的回文子串。
如果字符串的反序与原始字符串相同,则该字符串称为回文字符串。
示例 1:
1 2 3 输入:s = "babad" 输出:"bab" 解释:"aba" 同样是符合题意的答案。
示例 2:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 public class test1 { public static void main (String[] args) { System.out.println(longestPalindrome("babad" )); } public static String longestPalindrome (String s) { String maxStr = "" ; if (s.length() == 1 ){ maxStr = s; } for (int i = 0 ; i < s.length()-1 ; i++) { String step1 = part(s,i,i); String step = part(s,i,i+1 ); if (step.length() > maxStr.length()){ maxStr = step; } if (step1.length() > maxStr.length()){ maxStr = step1; } } return maxStr; } public static String part (String s,int begin,int end) { if ((begin >= 0 && end < s.length()) && s.charAt(begin)==s.charAt(end)){ return part(s,begin-1 ,end+1 ); }else { return s.substring(begin+1 ,end); } } }
33.搜索旋转排序数组(中等)
整数数组 nums 按升序排列,数组中的值 互不相同 。
在传递给函数之前,nums 在预先未知的某个下标 k(0 <= k < nums.length)上进行了 旋转 ,使数组变为 [nums[k], nums[k+1], ..., nums[n-1], nums[0], nums[1], ..., nums[k-1]](下标 从 0 开始 计数)。例如, [0,1,2,4,5,6,7] 在下标 3 处经旋转后可能变为 [4,5,6,7,0,1,2] 。
给你 旋转后 的数组 nums 和一个整数 target ,如果 nums 中存在这个目标值 target ,则返回它的下标,否则返回 -1 。
你必须设计一个时间复杂度为 O(log n) 的算法解决此问题。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:nums = [4,5,6,7,0,1,2], target = 0 输出:4
示例 2:
1 2 输入:nums = [4,5,6,7,0,1,2], target = 3 输出:-1
示例 3:
1 2 输入:nums = [1], target = 0 输出:-1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 public class test1 { public static void main (String[] args) { int [] nums = {4 ,5 ,6 ,7 ,0 ,1 ,2 }; System.out.println(search(nums,1 )); } public static int search (int [] nums, int target) { return part(nums,target,0 ,nums.length-1 ); } public static int part (int [] nums, int target, int begin, int end) { int mid = (end + begin)/2 ; System.out.println("begin->" +begin+" mid->" +mid+" end->" +end); if (begin == end || end - begin == 1 ){ if (nums[begin] == target) return begin; else if (nums[end] == target) return end; else return -1 ; } if (nums[begin] < nums[mid]){ if (nums[begin] <= target && target <= nums[mid]){ return part(nums,target,begin,mid); } } if (nums[mid] < nums[end]){ if (nums[mid] <= target && target <= nums[end]){ return part(nums,target,mid,end); } } if (nums[begin] > nums[mid]){ return part(nums,target,begin,mid); } if (nums[mid] > nums[end]){ return part(nums,target,mid,end); } return -1 ; } }
20.有效的括号(简单)
给定一个只包括 '(',')','{','}','[',']' 的字符串 s ,判断字符串是否有效。
有效字符串需满足:
左括号必须用相同类型的右括号闭合。
左括号必须以正确的顺序闭合。
每个右括号都有一个对应的相同类型的左括号。
示例 1:
示例 2:
示例 3:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 public class test1 { public static void main (String[] args) { System.out.println(isValid("(){}({})" )); } public static boolean isValid (String s) { int n = s.length(); if (n % 2 == 1 ) { return false ; } Stack<Character> stack = new Stack (); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { if (stack.size()!=0 && ((stack.peek()=='(' && s.charAt(i)==')' ) ||(stack.peek()=='{' && s.charAt(i)=='}' ) ||(stack.peek()=='[' && s.charAt(i)==']' ))){ stack.pop(); }else { stack.push(s.charAt(i)); } } return stack.size()==0 ; } }
121.买卖股票的最佳时机(简单)
给定一个数组 prices ,它的第 i 个元素 prices[i] 表示一支给定股票第 i 天的价格。
你只能选择 某一天 买入这只股票,并选择在 未来的某一个不同的日子 卖出该股票。设计一个算法来计算你所能获取的最大利润。
返回你可以从这笔交易中获取的最大利润。如果你不能获取任何利润,返回 0 。
示例 1:
1 2 3 4 输入:[7,1,5,3,6,4] 输出:5 解释:在第 2 天(股票价格 = 1)的时候买入,在第 5 天(股票价格 = 6)的时候卖出,最大利润 = 6-1 = 5 。 注意利润不能是 7-1 = 6, 因为卖出价格需要大于买入价格;同时,你不能在买入前卖出股票。
示例 2:
1 2 3 输入:prices = [7,6,4,3,1] 输出:0 解释:在这种情况下, 没有交易完成, 所以最大利润为 0。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public class test1 { public static void main (String[] args) { int [] test = {7 ,1 ,5 ,3 ,6 ,4 }; System.out.println(maxProfit(test)); } public static int maxProfit (int [] prices) { int min = prices[0 ]; int maxMoney = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < prices.length; i++) { min = Math.min(prices[i],min); maxMoney = Math.max(prices[i] - min,maxMoney); } return maxMoney; } }
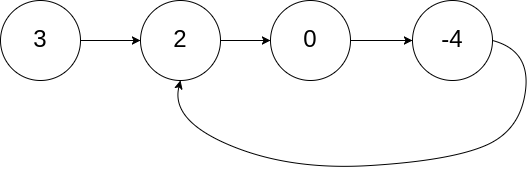
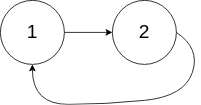
141.环形链表(简单)
给你一个链表的头节点 head ,判断链表中是否有环。
如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,评测系统内部使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。注意:pos 不作为参数进行传递 。仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。
如果链表中存在环 ,则返回 true 。 否则,返回 false 。
示例 1:
1 2 3 输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1 输出:true 解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
示例 2:
1 2 3 输入:head = [1,2], pos = 0 输出:true 解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第一个节点。
示例 3:
1 2 3 输入:head = [1], pos = -1 输出:false 解释:链表中没有环。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 public class test1 { public static void main (String[] args) { ListNode test1 = new ListNode (3 ); ListNode test2 = new ListNode (2 ); ListNode test3 = new ListNode (0 ); ListNode test4 = new ListNode (-4 ); test1.next = test2; test2.next = test3; test3.next = test4; test4.next = test2; System.out.println(hasCycle(test1)); } public static boolean hasCycle (ListNode head) { if (head==null ) return false ; ListNode s1 = head; ListNode s2 = head; while (s1.next != null && s2.next != null && s2.next.next != null ){ s1 = s1.next; s2 = s2.next.next; if (s1==s2) return true ; } return false ; } } class ListNode { int val; ListNode next; ListNode(int x) { val = x; next = null ; } }